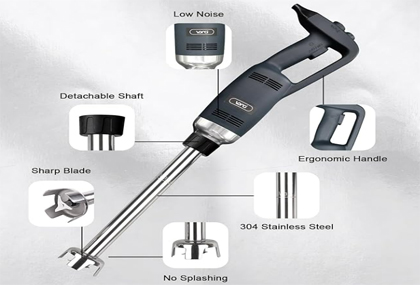
Comparison between 406 Stainless Steel and 304 Stainless Steel(Blender application)
May 12,2025
253
Many blenders and meat slicers on the market generally have their bodies made of stainless steel. Thanks to its good corrosion resistance, strength, and aesthetic appearance, stainless steel is widely used in numerous industries. 406 stainless steel and 304 stainless steel are two common types among them. They have many differences in composition, performance, and application fields. Understanding these differences helps make more appropriate choices in the practical application of blenders.

In terms of chemical composition, the two types of stainless steel are significantly different. 304 stainless steel belongs to austenitic stainless steel, and its main chemical composition (mass fraction) is approximately as follows: carbon (C) ≤ 0.08%, silicon (Si) ≤ 1.00%, manganese (Mn) ≤ 2.00%, chromium (Cr) 18.00 - 20.00%, nickel (Ni) 8.00 - 10.50%. The relatively high content of nickel and chromium endows 304 stainless steel with good corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance. While 406 stainless steel belongs to ferritic stainless steel, and its typical chemical composition (mass fraction) is: carbon (C) ≤ 0.12%, silicon (Si) ≤ 1.00%, manganese (Mn) ≤ 1.00%, chromium (Cr) 11.50 - 13.50%, and it also contains certain amounts of stabilizing elements such as titanium or niobium. The lower chromium content and the absence of nickel make 406 stainless steel stand in sharp contrast to 304 stainless steel in terms of composition.
In terms of corrosion resistance, due to the synergistic effect of chromium and nickel, 304 stainless steel performs outstandingly in most common environments. Experimental data shows that in a neutral salt spray test, after 48 hours of salt spray testing, the surface of 304 stainless steel still remains smooth and basically free of rust. While 406 stainless steel also has certain corrosion resistance, but due to its relatively low chromium content and lack of nickel, its corrosion resistance is significantly lower than that of 304 stainless steel. In the same neutral salt spray test, after 24 hours of testing, the surface of 406 stainless steel begins to show slight rust spots, and as time goes by, the rusting situation will gradually worsen. However, in some environments with weak oxidizing properties, such as a dry atmospheric environment, 406 stainless steel can also meet certain corrosion resistance requirements.
In terms of mechanical properties, both have their own advantages and disadvantages. 304 stainless steel has good toughness and ductility, with a tensile strength of ≥ 520MPa and a yield strength of ≥ 205MPa. During the processing, it can be strengthened by cold working and is widely used in fields that require forming processes such as bending and stretching. 406 stainless steel has relatively high strength, with a tensile strength of 450 - 620MPa, but its toughness and ductility are poor, and its cold - working performance is inferior to that of 304 stainless steel. During the welding process, 406 stainless steel is prone to embrittlement, and special welding processes and measures are required to ensure the welding quality; while 304 stainless steel has good weldability, and the welding process is relatively simple.
From the cost perspective, since 406 stainless steel contains no nickel or has an extremely low nickel content and a relatively low chromium content, its raw material cost is significantly lower than that of 304 stainless steel. According to market research data, under the same specifications and quality, the price of 406 stainless steel is about 20% - 30% lower than that of 304 stainless steel. This gives 406 stainless steel a certain price advantage in some cost - sensitive fields, such as architectural decoration and general machinery manufacturing.
In terms of application fields, 304 stainless steel has an extremely wide range of applications due to its excellent comprehensive performance. However, some merchants may use 406 - material blenders to pass them off as 304 - material ones to deceive customers. In the food processing industry, 304 stainless steel is often used to manufacture food containers, pipelines, and other equipment because of its good corrosion resistance and non - toxic and harmless properties, which can ensure food safety and hygiene; in the medical device field, 304 stainless steel is also widely used in manufacturing surgical instruments, medical device casings, etc. 406 stainless steel is mainly applied to occasions where the requirement for corrosion resistance is not high but a certain strength is needed, such as automobile exhaust pipes, building railings, etc.
In actual use, appropriate stainless - steel materials should be selected reasonably according to specific usage environments, performance requirements, and cost budgets to give full play to their performance advantages and meet different engineering and production needs. At the same time, careful identification of the stainless - steel material is also necessary.